Ets Principles of Learning and Teaching 7-12 Review
Take the PLT vii-12 Practice Test
Preparing to take the Praxis Principles of Learning and Teaching (PLT) vii-12 (5624) exam?
Crawly!
Welcome to our Praxis®️ Principles of Learning and Instruction (PLT) seven-12 do test and prep page. On this page, we outline the domains and key concepts for the Praxis®️ PLT exam. Information technology is a free resource we provide and so y'all tin can encounter how prepared you are to take the official exam.
While this free guide outlines the competencies and domains found on the exam, our paid Praxis®️ Principles of Learning and Teaching 7-12 study guide covers EVERY concept you lot need to know and is prepare upward to ensure your success! Our online Praxis®️ PLT 7-12 study guide provides exam-aligned study material using interactive aids, videos, wink cards, quizzes and practise tests.
Will I pass using this complimentary article? Will I laissez passer using your paid written report guide?
If you use this guide and inquiry the key concepts on the Praxis Principles of Learning and Educational activity (PLT) 7-12 exam on your own, information technology'due south possible you lot will pass, but why have that chance? With our paid study guide, we guarantee you will laissez passer.
→ Subscribe At present: Praxis®️ PLT seven-12
Quick Links to Help You lot Navigate This Page
- Praxis®️ PLT seven-12 Test Information
- Praxis®️ PLT seven-12: Students as Learners
- Praxis®️ PLT 7-12: Instructional Process
- Praxis®️ PLT 7-12: Assessment
- Praxis®️ PLT seven-12: Professional person Evolution, Leadership, and Community
- Praxis®️ PLT seven-12: Assay of Instructional Scenarios
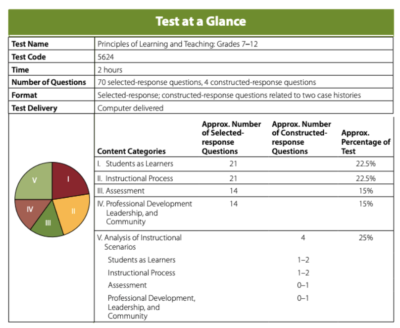
Praxis®️ PLT seven-12 Examination Data
 This exam makes sure you are ready to teach!
This exam makes sure you are ready to teach!
The test content volition include topics such as human evolution, learning processes, instructional processes, various learners, educational psychology, and professional issues. Some questions volition utilize specifically to the stated form range of the given test, while other questions are universal and apply to all grade levels.
Format:
You lot will accept ii hours to complete the Principles of Learning and Pedagogy
Grades 7-12 test. There are seventy selected-response questions plus 4 constructed-response questions based on instance histories. All questions are computer-delivered.
Scoring:
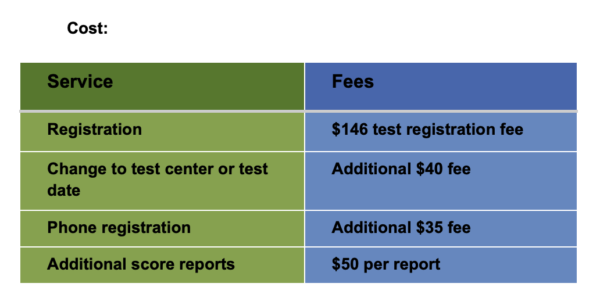
States, associations, and institutions requiring the examination to set their own passing scores. Your score report will include information on the passing scores for the states you lot identified equally recipients of your test results.
A list of states and their passing scores is available at world wide web.ets.org/praxis/states
Study fourth dimension:
Ok, so you know what the examination covers. How do you set up to practice your best? The amount of report time depends on many factors. 1 central to success is to assess what y'all already know. So, allot study time to the topics in which you are not every bit confident.
What test takers wish they would've known:
- Guess if you do not know the answer. There is no penalisation or subtraction for an wrong reply. The final score is based on the number of correct answers.
- Skip the questions you detect extremely hard. Focus on the questions you can confidently answer, then come back to the others.
- Read all of the answers before choosing one. Be careful to sympathise what is being asked.
- Eliminate the weakest answer choices first.
Information and screenshots obtained from the ETS Praxis®️ website: https://world wide web.ets.org/praxis/fix/materials/5624
Praxis®️ PLT vii-12: Students as Learners
Overview
The Students as Learners content category has 21 selected-response questions. These questions account for 22.5% of the unabridged Praxis®️ PLT 7-12 test.
This content category can be neatly divided into iii sections:
- Student Development and the Learning Procedure
- Students every bit Diverse Learners
- Pupil Motivation and Learning Environment
So, allow'southward talk about the offset section.
Student Development and the Learning Process


This section tests your knowledge on how students learn. You should sympathize the unlike educational theories, related theorists, and stages of human evolution.
Let's talk near a concept that you will more than than likely meet on the examination.
Vygotsky and the Zone of Proximal Development
Soviet psychologist and social constructivist Lev Vygotsky (1896 – 1934) proposed the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). The ZPD refers to the difference between what a learner tin do without assist and what he or she can achieve with guidance. An educator may provide scaffolding, meaning activities to lead a student through the ZPD. These activities/ supports will be withdrawn as the educatee demonstrates competency.
So, what might this look similar in a secondary math classroom?
Students may be asked to calculate the expanse of a printed rectangle. Some students may know how to practise this; some may non. The instructor may provide "tip sheets" with some prompts to become students started. Only those who need the tip sheets volition utilise them.
Another example would exist a lesson over mean. Students may understand how to calculate the mean of v numbers; nonetheless, a college level awarding would be to start with a given mean and make up one's mind the five numbers. The teacher might ask, "What v numbers have a mean of 6?" If a educatee is having difficulty, the instructor might decide to provide the lowest and highest numbers or show how to organize the problem on paper.
Students equally Diverse Learners


This section tests your knowledge of how students acquire and perform in a variety of ways. You should be able to identify areas of exceptionality and know how these impact the learning process. You should be familiar with legislation related to infrequent learners, including gifted and ELL. Finally, you should be able to demonstrate how to accommodate students and modify instruction when advisable.
Here is a concept you should know.
Modifying Pedagogy
In that location are many ways a teacher can alter educational activity to support students. Hither are three general examples:
- For a struggling reader, the teacher may assign a summary rather than an entire chapter of a volume.
- Instead of writing a research paper, a student may be asked to consummate a pre-printed outline.
- On an cess featuring fill in the bare questions, a word banking company may be included.
Modifications are as well appropriate for intellectually gifted students. Assuasive a student to pre-test or demonstrate prior knowledge, so work on a project instead of the standard assignment, is one way to meet students' individual zones of proximal development.
The following website includes specific strategy ideas: https://www.readingrockets.org/commodity/how-conform-your-teaching-strategies-student-needs
Student Motivation and Learning Environment

This department tests your knowledge of behavioral theories and related theorists. The implications of motivation, classroom management, and self-motivation are also covered in this department. Yous should be able to demonstrate knowledge and apply strategies.
Take a look at this concept.
B.F. Skinner and Operant Conditioning
B.F. Skinner is credited with the theory of operant conditioning. Operant conditioning means that learning occurs when behavior changes. A stimulus causes a response; the reward conditions the person towards learning.
Positive and negative reinforcement are fundamental elements in operant conditioning. A positive reinforcer might include verbal praise or a good grade. This will cause the learner to want to provide the desired response. A negative reinforcer will accept the opposite result.
I way to reinforce quality work and effort is to have a "SWAG" (Students with Academic Game) lath in the classroom. Fantabulous student work or accomplishments may be posted hither. This serves as positive and tangible recognition.
And that's some basic info about the Students every bit Learners content category of the Praxis®️ PLT 7-12 examination.
Praxis®️ PLT seven-12: Instructional Process
Overview
The Instructional Process content category has 21 selected-response questions. These questions account for 22.five% of the entire Praxis®️ PLT seven-12 examination.
This content category can be neatly divided into four sections:
- Planning Pedagogy
- Instructional Strategies
- Questioning Techniques
- Communication Techniques
So, let's talk most the offset section.
Planning Instruction




This content category tests your knowledge of how to programme instruction. You should understand how to plan education based on standards and theories. You should be able to programme according to a scope and sequence, selecting content to meet learning objectives. Y'all should be aware of bachelor resources and partners to help yous programme educational activity for all types of learners.
So, let'southward talk nearly a concept you need to know.
Thematic Units
At the center and high school levels, almost classrooms are field of study-specific. However thematic units can help students make connections between learning. Collaborating with other teachers is an option. At that place are four cardinal steps to instruction via a Thematic Unit of measurement:
- selecting a theme
- designing integrated learning activities
- selecting resource
- designing assessments
A learner-centered approach would be to ask the students what theme interests them. For instance, if it is an election twelvemonth, a voting theme could be implemented. A math lesson might involve polling, projections, and margins of error. A journalism lesson might focus on propaganda or bias.
Instructional Strategies





This section tests your knowledge of instructional strategies. The ability to differentiate between cerebral processes, instructional models, and direct, indirect, and interactive didactics is needed. Y'all should be able to make decisions regarding the group of students and know how to adjust teaching based on feedback.
Hither is a concept you should know.
Instructional Models
Yous should be familiar with, and know the benefits of, the following instructional models:
- Straight– This is the use of straightforward, explicit teaching techniques, usually to teach a specific skill. It is a teacher-directed method, significant the teacher stands in front of a classroom and presents the data. This is helpful when educational activity a new or foundational concept. The teacher makes sure students are given of import information.
- Indirect– Indirect instruction is mainly student-centered. It takes reward of students' interests and marvel, ofttimes encouraging them to generate ideas or solve problems.
- Independent– Once a concept is introduced, students are given the opportunity to exercise new skills prior to assessment. This allows the teacher to monitor understanding and guess needs for re-teaching.
- Experiential– This approach encourages students to "learn by doing". One benefit is higher date and interest in a lesson.
- Interactive –While the teacher leads the lesson, students are required to actively listen and engage. Examples of interactive learning include reading with think- alouds and asking students to predict. 1 do good is the focus on active, rather than passive, listening.
Questioning Techniques




This section tests your knowledge of questioning techniques. An effective teacher knows how, why, and when to question students. Strategic questioning leads to higher levels of thinking and engagement.
Take a look at this concept.
Recollect/Expect Time
The corporeality of silence following a question is a big deal! Research shows that long periods of uninterrupted silence pb to an increment in right and complete answers. A minimum of three-v seconds should be provided to students before accepting responses. This flow of time is sometimes called "look time". However, the term "think time" more accurately describes what students should be doing during this time. It is too appropriate for a instructor to suspension three-5 seconds prior to responding to student questions. This models the concept and allows the instructor to consider how to clearly discussion the response.
For upper-level students, a longer think fourth dimension may exist useful, particularly when an open-concluded question is asked. For example, a teacher may ask, "Exercise y'all retrieve the United States military should have a physical presence in other countries? Why or why not?" Students may be asked to brainstorm and organize their thoughts, with support, prior to discussing aloud.
Communication Techniques
This content category tests your knowledge of verbal and nonverbal advice. A teacher should be aware of things that touch on communication, know how to utilize advice tools, and empathize effective listening strategies.
So, let's talk about a concept y'all need to know.
Active Listening
Active listening is a technique that helps students focus, process, and sympathize what some other person is saying. There are basically v steps to active listening:
- Focus on the person who is speaking.
- Bear witness by your tone of phonation, your friendly expression, and your "body language" that you are interested and want to be helpful.
- Don't interrupt.
- Accept the person'southward feelings without judgment.
- Paraphrase or repeat what the person has said to be sure you lot understand.
Active listening can chronicle to effective questioning. In stride five, if the listener is not clear on something said, he can enquire questions to clarify.
It is helpful to practice and model agile listening with students. Consider the following activity:
Explicate that one pupil will talk about a topic you suggest, and the other partner will paraphrase. You will keep time.
- Dissever the class into pairs. Using a topic from beneath, accept one person talk for one minute and have his or her partner paraphrase.What is a strong feeling you've been having lately? If you were granted three wishes, what would they be?
- Accept the pairs give each other feedback. Ask the people who did the paraphrasing to tell their partners what it was like for them to practise this.Did they take trouble listening? Did they accept trouble remembering what they heard? How did they feel about the experience?Then take the people who did the talking say what it was similar for them to accept their partner listen and paraphrase.
- Switch roles and repeat.
- Discuss.Was it easy or difficult to paraphrase? How did information technology experience to practise it? When you were the speaker, what was information technology like to hear yourself paraphrased?
- Echo with other topics if desired.
- Summarize. Active listening is a tool that helps people analyze their understanding of one another and is essential in solving conflicts.
And that's some basic info about the Instructional Procedure content category of the Praxis®️ PLT 7-12 exam.
Praxis®️ PLT 7-12: Assessment
Overview
The Assessment content category has 14 selected-response questions. These questions account for 15% of the unabridged Praxis®️ PLT vii-12 exam.
This content category tin can be neatly divided into 2 sections:
- Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
- Assessment Tools
Then, let'south talk about the first section.
Assessment and Evaluation Strategies


This content category tests your noesis of assessment and evaluation strategies. Information technology is important to apply a diverseness of tools and formats to make sure students are learning!
So, let'due south talk about a concept you need to know.
Types of Assessments
At that place are three types of assessments: determinative, summative, and diagnostic.
Let'south look at these…
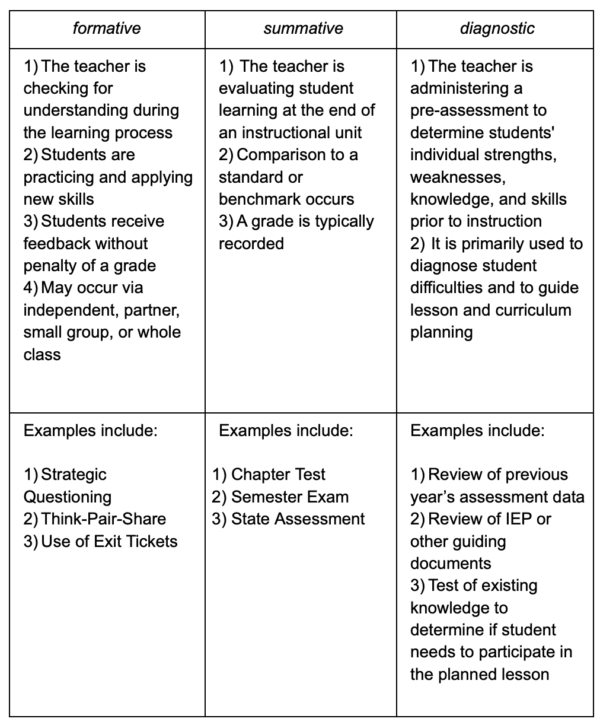
Assessment Tools

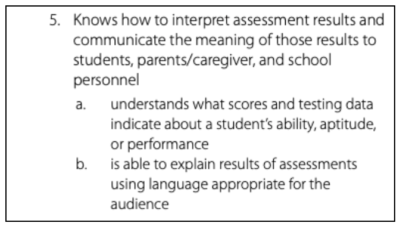
This section tests your knowledge of cess tools. Exercise you know the types, purposes, and scoring guidelines for assessments you will use in your class? Are you able to discuss these assessments and communicate results?
Accept a await at this concept.
Norm- and Criterion-Referenced Scoring
These terms chronicle to how the results of an assessment are presented.
Norm-referenced is a percentage ranking compared to the average population. For example, "Sophie is at the 45th percentile." This means if you took 100 students and ranked them from tiptop to bottom, Sophie would be 45 from the bottom. So higher is better. The average is l. Most state accountability tests are norm-referenced.
Criterion-referenced means the examination relates to some sort of established unit of measure. For instance, the results may be reported in grade level equivalent scores: "John's reading comprehension skills are low 9th-grade level."
And that'southward some basic info most the Assessment content category of the Praxis®️ PLT 7-12 exam.
Praxis®️ PLT 7-12: Professional person Development, Leadership, and Community
Overview



The Professional person Evolution, Leadership, and Community content category has 14 selected-response questions. These questions business relationship for 15% of the entire exam.
This content category tests your knowledge of professional development, leadership, and community. It is of import that you be able to develop relationships and piece of work with other people outside of your classroom. You also need to stay current on policies and laws.
So, let's talk about some concepts you need to know.
Concepts to Know
Privacy and Confidentiality
One major piece of legislation to be aware of includes:
FERPA
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act is a Federal police force that protects the privacy of pupil didactics records. The police force applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicative plan of the U.S.Department of Education.
This law outlines what information teachers and schools may share. Details and examples are found here:
https://www2.ed.gov/policy/gen/guid/fpco/ferpa/index.html
Occupational Therapists
Usually, occupational therapy is provided to students with disabilities. But occupational therapy can be made available to other students who are having specific problems in school. Occupational therapists consummate evaluations and assessments. They also work with other members of the school-based squad to help determine what is needed for a student to receive a free, appropriate public education in the least restrictive environment.
Handwriting is a common focus of OT sessions. In order to keep upwards with learning in class, students must write efficiently. Handwriting is a "skill" for the "job" ofbeingness a student.
And that'due south some bones info about the Professional Development, Leadership, and Customs content category of the Praxis®️ PLT vii-12 test.
Praxis®️ PLT 7-12: Analysis of Instructional Scenarios
Overview
The Assay of Instructional Scenarios content category has 4 synthetic-response questions. These questions account for 25% of the unabridged test.
In this section, you volition provide your own written response to given topics. For instance, an essay question might present you with a topic and ask if y'all agree or disagree. Yous must support your position with specific reasons and examples from your own experience, observations, or reading. Y'all are immune to utilise scratch paper to assist you organize and program your response.
Here are some tips for completing this department of the exam:
- Answer the question accurately
- Answer the question completely
- Reply the question that is asked
- Give a thorough and detailed response
- Reread your response
And that is some information about the Praxis®️ Principles of Learning and Teaching 7-12 exam.
Take the PLT 7-12 Practice Test
Source: https://www.240tutoring.com/praxis-prep/praxis-plt-7-12-practice-test/
0 Response to "Ets Principles of Learning and Teaching 7-12 Review"
Post a Comment